Warnings¶
Warning
Before using the delete feature, we strongly recommend running several dry runs to get acquainted with mediacurator, as incorrect usage can cause irreversible damage to your media library.
The –delete flag will permanently delete files, so it is crucial to ensure that the command is executed correctly. Below are some examples of how the delete feature works.
Example use cases for the –delete Flag¶
Delete all non-HD (low-resolution) videos in a folder:
mediacurator list --delete --filters lowres --dirs "/mnt/media/"
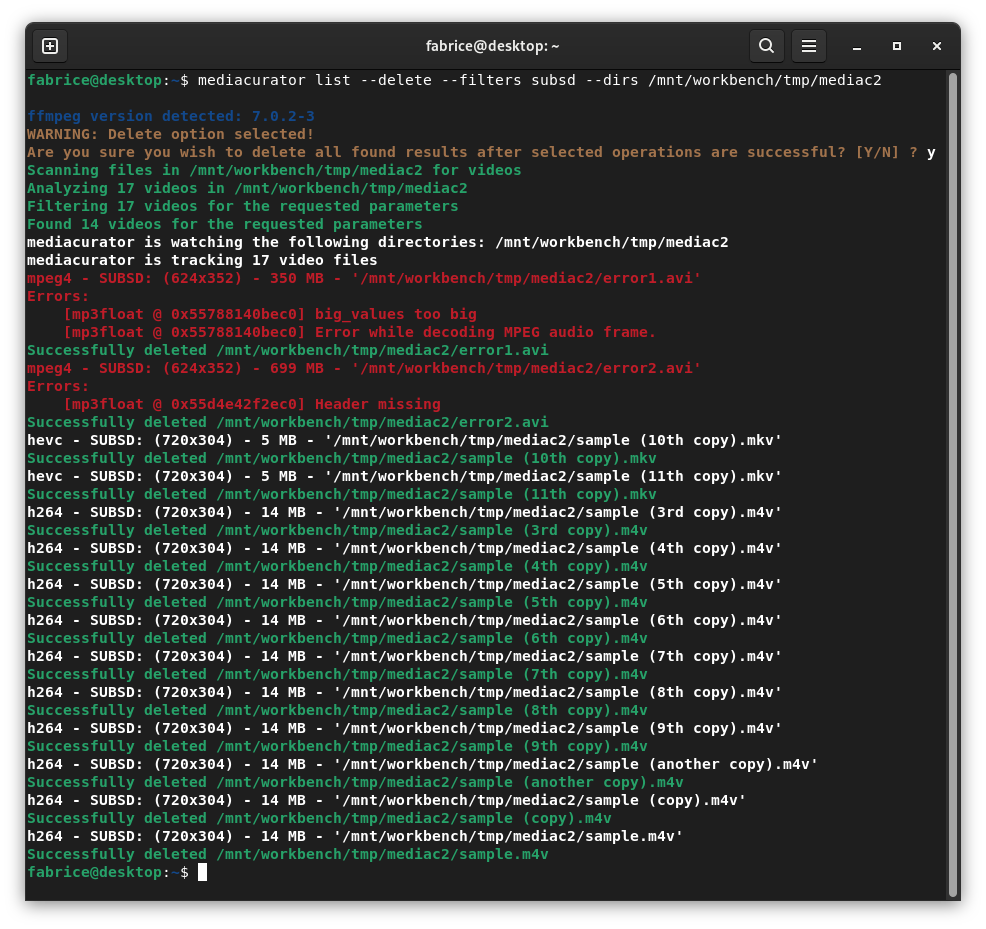
Delete all substandard quality videos in a folder:
mediacurator list --delete --filters subsd --dirs "/mnt/media/"
Delete all videos in a folder with encoding errors:
mediacurator list --delete --filters fferror --dirs "/mnt/media/"
Convert (repair) and then delete all videos in a folder with encoding errors:
mediacurator convert --delete --filters fferror --dirs "/mnt/media/"
Delete all videos in a folder:
mediacurator list --delete --dirs "/mnt/media/"
Important Notes¶
Irreversibility: All of these commands involve permanent deletion. Once a file is deleted using the –delete flag, it cannot be recovered.
Run without `–delete` first: Always perform several dry runs by omitting the –delete flag to ensure that the correct files are selected for deletion. Familiarizing yourself with the tool before using destructive commands is essential to avoid unintended consequences.
Specific File Selection: If you’re unsure about applying filters to an entire directory, you can use the –files option to target individual files for deletion or conversion, further reducing the risk of unintended deletions.
Backup Recommendation: Before running any commands with the –delete flag, it is a good practice to back up your media library or the specific directories being processed, especially if they contain valuable or irreplaceable files.
Dry run example (without deletion)¶
mediacurator list --filters lowres --dirs "/mnt/media/"
Make sure you carefully verify the output and files selected during the dry runs to prevent accidental data loss.
